22.02.07 - Entity Relationship Modelling
Database Design
- Can create a design that is independent of DBMS
- Often results in a more efficient and simpler queries once the database has been created
Entity/Relationship Modelling
Used for Conceptual design
- Entities - objects or items of interest
- Attributes - properties of an entity
- Relationships - links between entities
Represented as E/R diagrams that
- Give a conceptual view of the database
- Independent of the choice of DBMS
- Identify some problems in a design
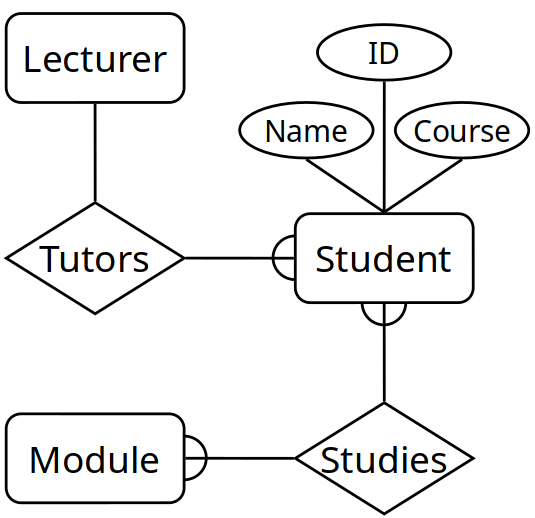
Entities
Represent objects or things of interest. Physical things or more abstract things Entities have:
- General types or class
- Instances of that particular type
- Attributes
Have attributes, but attributes have no smaller parts Can have relationships between them, but an attribute belongs to a single entity Represent Entities as boxes with rounded corners. Labelled with the names of the class of objects represented by that entity
Attributes
Facts, aspects, properties or details about an entity Attributes have:
- A name
- Associated entity
- Domains of possible values
- Each instance of the associated entity, a value from the attributes domain
Attribute belongs to a single entity Represented as ovals. Linked to its entity by a line. Name of the attribute is written in the oval.
Relationships
Are an association between two or more entities Relationships have:
- Name
- Set of entities that participate in them
- A degree - number of entities that participate
- Cardinality Ratio
Cardinality Ratios
Each entity in a relationship can participate in zero, one, or more than one instances of that relationship
- One to One (1:1)
- One to Many (1:M)
- Many to Many (M:M)
Relationships are shown as links between two entities Name is given in a diamond box. Ends of the link show cardinality
Making E/R Models
Need to identify:
- Entities (Nouns)
- Attributes (Nouns, facts or properties)
- Relationships (Verbs, between two entities)
- Cardinality Ratios Obtain these from a problem description
Removing M:M relationships
Many to Many relationships are difficult to represent in a database Can split a many to many relationship into two one to many relationships by creating an additional entity
Entities can have attributes but attributes have no smaller parts Entities can have relationships between them, but an attribute belongs to a single entity
1:1 Relationships
Some relationships between entities, A and B, might be redundant if
- It is a 1:1 relationship between A and B
- Every A is related to a B and every B is related to an A
Debugging Designs
E/R diagrams can be used to plan queries. If cant find useful information from diagram, need to change the design