Interfaces, Buttons and Event Handlers
Design Patterns
Patterns
- Patterns help us to identify ways in which a problem can be solved
- Can identify the problem
- Look at how people have solved this in the past
- Much less 'thinking' and 'working out'
- Avoid potential pitfalls later on
- Usually many good ways to solve a problem
Layout managers
- Containers ask their layout manager to do the work
- Container calls functions in the base class Layout Manager
- Positioning of components
- Key design pattern feature: the container has delegated some of its work to another class - the layout manager
Strategy Pattern
- This is a Behavioural Pattern
- Allow objects behaviour to change at runtime
- Strategies should be interchangeable
- Should be same regardless of layout manager
(Sub-type) Polymorphism and Interfaces
- Normally hide the data inside the class, and expose some kind of interface to the outside world
- When using polymorphism to allow behaviour to be changed at runtime, don't care how it is implemented inside the class
- Only care what functions/methods are available
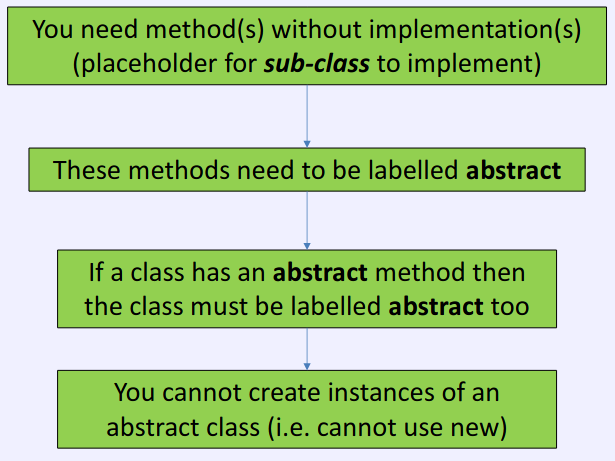
- An abstract method is a method without implementation
Summary
Interfaces
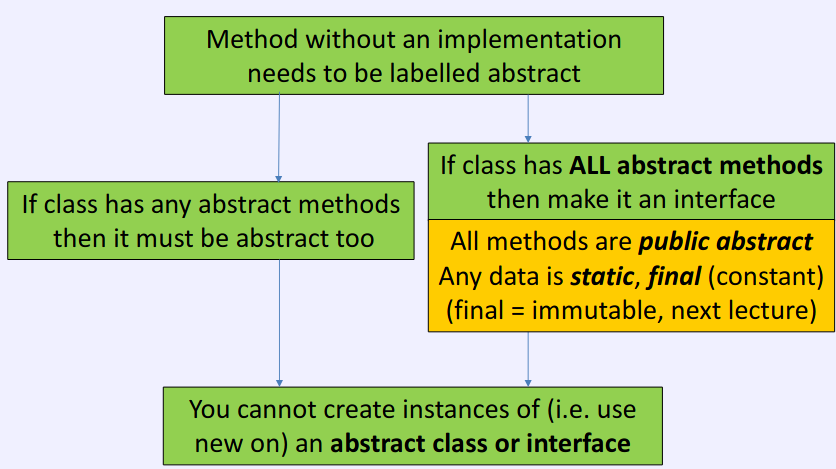
- If not have implementations for any of the methods, can use an interface instead of a class
- Interface is a set of functions without implementations
- Sub class MUST implement ALL functions (or be abstract)
- Subclass implements interfaces but extends a class
- Class can only extend one class
- Can 'implement' many interfaces
JButtons
- Java Swing uses the Observer Pattern to monitor event handlers
- Uses an interface, the ActionListener
- An interface is just an abstract class which can use as a superclass
Observer Pattern
- Is a common pattern to use when we want to notify other objects that something has happened
- Object to notify supports some interface (Observer)
- Notifying object keeps a list/array/etc of there to notify
- Notifying object considers these as the base class/interface and calls a method
JButton
To handle key presses, JButton needs an object to tell