1. Pointers & Data Types
02/02/23
Data Types
bool - true/false. bool and int can be converted implicitly/automatically. non-zero is defined to be true. Can use this inside a while loop;
int x = 6;
while(x)
{
printf("X is %d\n",x);
x-=2;
}
Size of types
Size of types can vary based on compilers/operating system. Some guarantees are given:
- Minimum size (bits) -
char8,short16,long32. - Relative sizes -
charshortintlong
void - type is used to mean no return value, no parameters, optional. Cannot create a variable of type void
const - means constant/unchangeable. Use const char * instead of char*
auto - Allows you to be lazy, don't bother about type. Can only be used for initialised variables.
Pointers
& - Ask for the address of a variable
sizeof() - Size in chars - compile time
* - Used to denote a pointer. The value of the pointer is an address in memory. The type of a pointer says what type of data the program should expect to find at the address
Can think of pointers whichever what is easier for you
- As an address in memory and a type/format
- As a way of pointing to some other data, and a record of what type of data you think the thing pointed as is
Dereferencing operator *
The * operator is used to access the thing that a pointer points at.
char c1 = 'h';
char* pc = &c1; //pc is a pointer to c1
char c3 = *pc; // *pc is thing pointed at
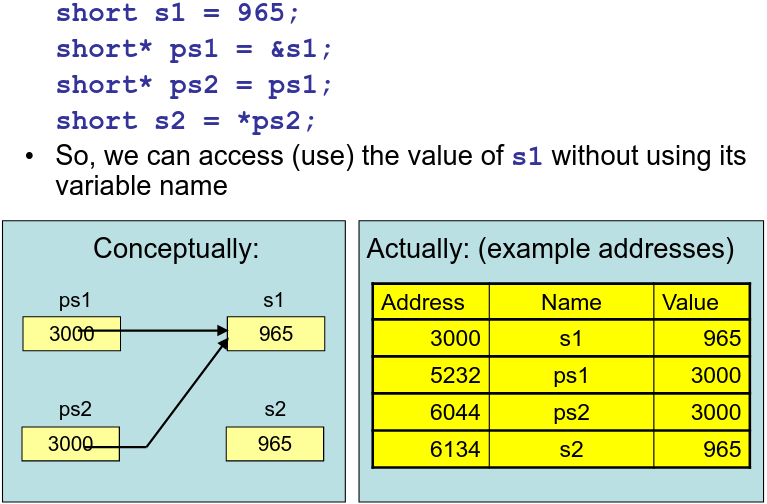
Uninitialised Pointers
Variables are NOT initialised unless you give them an initial value. Value of one is undefined.
Passing pointers as parameters
Each parameter has a single type, so may be one thing. A copy of this is stored in memory for the parameter. To alter something that is external to a function from within a function, need to refer to the thing itself, not a copy of it.
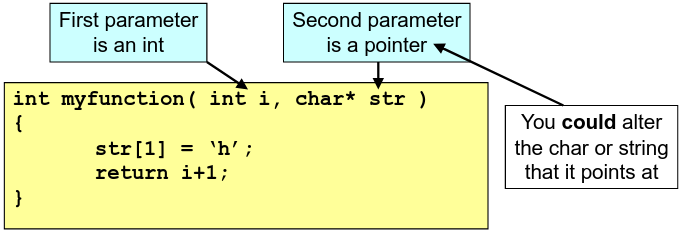
void AlterCopy( int icopy )
{
icopy = 2;
}
void AlterValue( int* picopy )
{
*picopy = 3;
}
int main( int argc, char* argv[] )
{
int i = 1;
printf( "Initial value of i is %d\n", i );
AlterCopy( i );
printf( "After AlterCopy, value of i is %d\n", i );
AlterValue( &i );
printf( "After AlterValue, value of i is %d\n", i );
return 0;
}