0. Client-Server Java
31/01/23
Distributed System - Hardware or software components located at network computers communicate and coordinate their actions only by passing messages. They are everywhere!
Most applications are based on sharing resources. This is pervasive, powerful and often taken-for-granted feature of networked computer systems.
- Physical - printers, disk, computers
- Data - resources, documents, databases, webpages
- Computational/algorithmic - Search engines, or machine-learning algorithms
Services
- Distinct part of a computer system that manages a collection of related resources and presents their functionality to users and applications.
- Runs on a specific machine which physically hosts the managed resources
- Provides a specific and controlled interface - usually over a network
- Many distributed systems consist only of clients making requests to servers to access/alter the resources managed by that service
Summary
- Distributed system is one in which hardware or software components located at network computers communicate their actions by passing messages
- Typically distributed systems are build around sharing of resources, whether physical or informational
- Resources are typically encapsulated and selectively exposed over the network as services that are accessed by clients.
- Clients and servers are typically both OS processes, and communicate directly with each other
Java Socket Programming
Messages are sent and received via sender and receiver queues/buffers. Sender performs a send operation; receiver a receive operation. Each endpoint is represented by a socket
Sockets
- Provides an abstract representation of a communication endpoint within a process (TCP, UDP)
- To send and receive messages a (TCP/UDP) socket must be bound to a specific port
- A single process can have many sockets, but only one TCP server or UDP socket on a host can be bound to a given port at any time
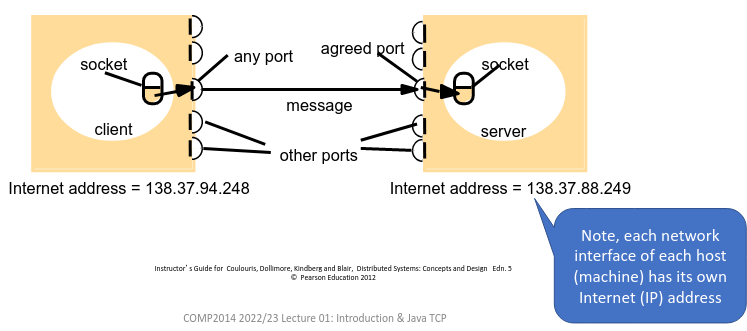
Message Destinations
- Send to the pair (Internet address, port number)
- If a clients identifies a server using a specific IP address then the server must always have that IP address
- If clients use names then a name service is used to translate this to network location at run time
Address Resolution - Every OS also provides an API for host name resolution. Internally the host will us DNS and/or other name services to look up the corresponding IP address
Summary
- Socket represents a TCP or UDP communication end-point within a process
- A name resolution API is needed
Java TCP programming
ServerSocket- Represents a server TCP socket. Binds to a particular portSocket- Represents one end of a TCP connection- Created by a client with a specified server IP address and port number
- Has a
java.io.InputStreamto receive bytes from andjava.io.OutputStreamto send bytes to
TCP Considerations
- Message Size - Application reads/writes any number of bytes at a time until the connection is closed
- Message Destination - A server can accept connection requests from any client
- Blocking - Limited amount of data is buffered at sender and receiver sockets and sends will block once the sender buffer is full
- Failure Model - Communication is reliable short of complete failure
- Lost messages are automatically re-transmitted. If not resolved within a time limit, whole connection fails
- Duplicate packets are discarded and out-of-order packets are reordered using sequence numbers
- Uses - Everything required to transfer data reliably and/or in large amounts (HTTPS, SSH, FTP, SMTP)
Summary
- TCP provides a reliable connection-oriented bidirectional byte-based stream service
- Java API comprises of
java.net.Socketandjava.net.ServerSocket