Natural Language Processing
Overview of NLP
Why Language
Language is the basis of interaction
Natural Language Understanding - Finding insights and understanding from text Natural Language Generation - Generating text for a purpose
Language is the key to interaction
- Interaction between people, machines, between machines etc Advances in speech recognition and speech generation (thanks to deep learning) brought natural language interfaces back Natural language -> languages which naturally evolved over time
Natural Language Understanding
- NLU systems focus on analysing natural language
- Humans are obsessive hoarders of data
- We can gain insights from the text data
Natural Language Generation
- NLG systems focus on generating natural language
- From chatbots
- Structured data
- Media data etc
NLP: the early years
- Focused on Rule-Based Systems
- Extract elements from text with regular expressions
- Classify text in a category based on lexicons
- Use conditions, extracted elements, and rules to build dynamically generated reports to send to users
- Rule-based systems are still used today, because they are reliable, easy to understand and require no data
Better computers brought a new obsession with benchmarking
Then deep learning craze appeared.
Common subfields of NLP
- Opinion mining, sentiment analysis
- Argument Stance Detection
- Recognising Textual Entailment
- Automated Summarisation
- Question Answering
- Information Retrieval
- Conversational User Interfaces
The NLP Pipeline
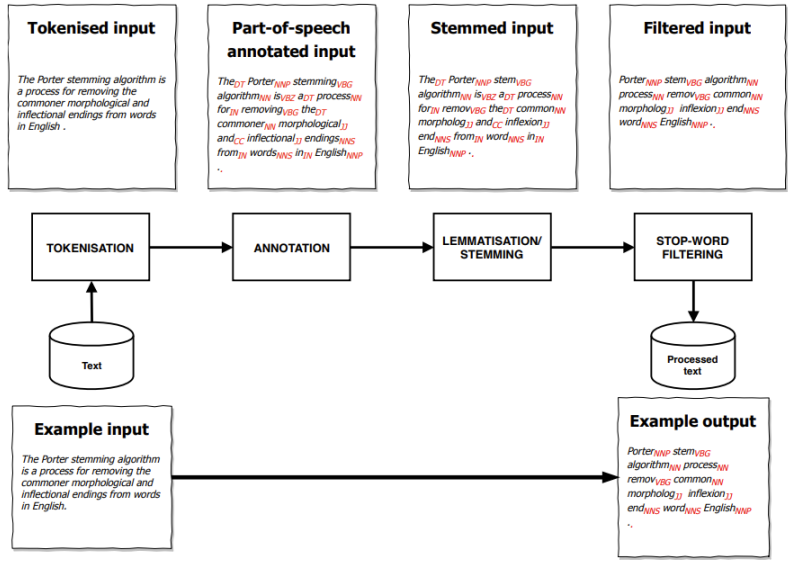
Preliminary notions
- Each unit of interest that we analyse is a document
- A collection of documents on interest in a corpus
1. Tokenisation
- A document is made of tokens
- Tokens can be of arbitrary length
2. Annotation (Part of Speech)
- Part of speech tagging gives each word their grammatical function in a sentence
- Different languages have different parts of speech
- Different POS parsers have different POS tags for the same language
- POS tags help disambiguate meaning using grammatical context
3. Word standardisation
- Words are inflected during usage
- Lemmatisation: Reducing terms to their lemma (dictionary form)
- Dogs, Dog, dog = dog.
- Produces more consistent content, but is slower
- Often requires text to be Part of Speech-annotated
- Stemming: Reducing terms to their word stem (common part of the inflections)
- programming = program, programmer = programm
- Stemming produces a list of words that don't exist, but is faster
- Simply runs a bunch of transformations on character strings
4. Filtering: stop words
- Not all words matter equally
- Some words are noise (e.g. determinants)
- Want to use a smaller vocabulary
- Less important words are kept in stop-lists
- We can also filter words by frequency
Pairs of words
- Set of consecutive words is called an n-gram
- Unigram: single word
- Bigram: two consecutive words
- Trigram: three consecutive words
- 4-gram: 4 consecutive words
- etc
- Only limited by sparsity of representation