1. Network (and virtualisation)
03/02/23
Networking
- Networks are complex and use the layering pattern:
- lower layers provide services that higher layers build on
- We'll focus on the Internet and the layered model that it uses
| Internet Model | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Application |
| 4 | Transport (TCP/UDP) |
| 3 | Internet (IP) |
| 2 | Network interface/Link |
| 1 | Physical |
| ISO Model | |
|---|---|
| 7 | Application |
| 6 | Presentation |
| 5 | Session |
| 4 | Transport |
| 3 | Network |
| 2 | Data Link |
| 1 | Physical |
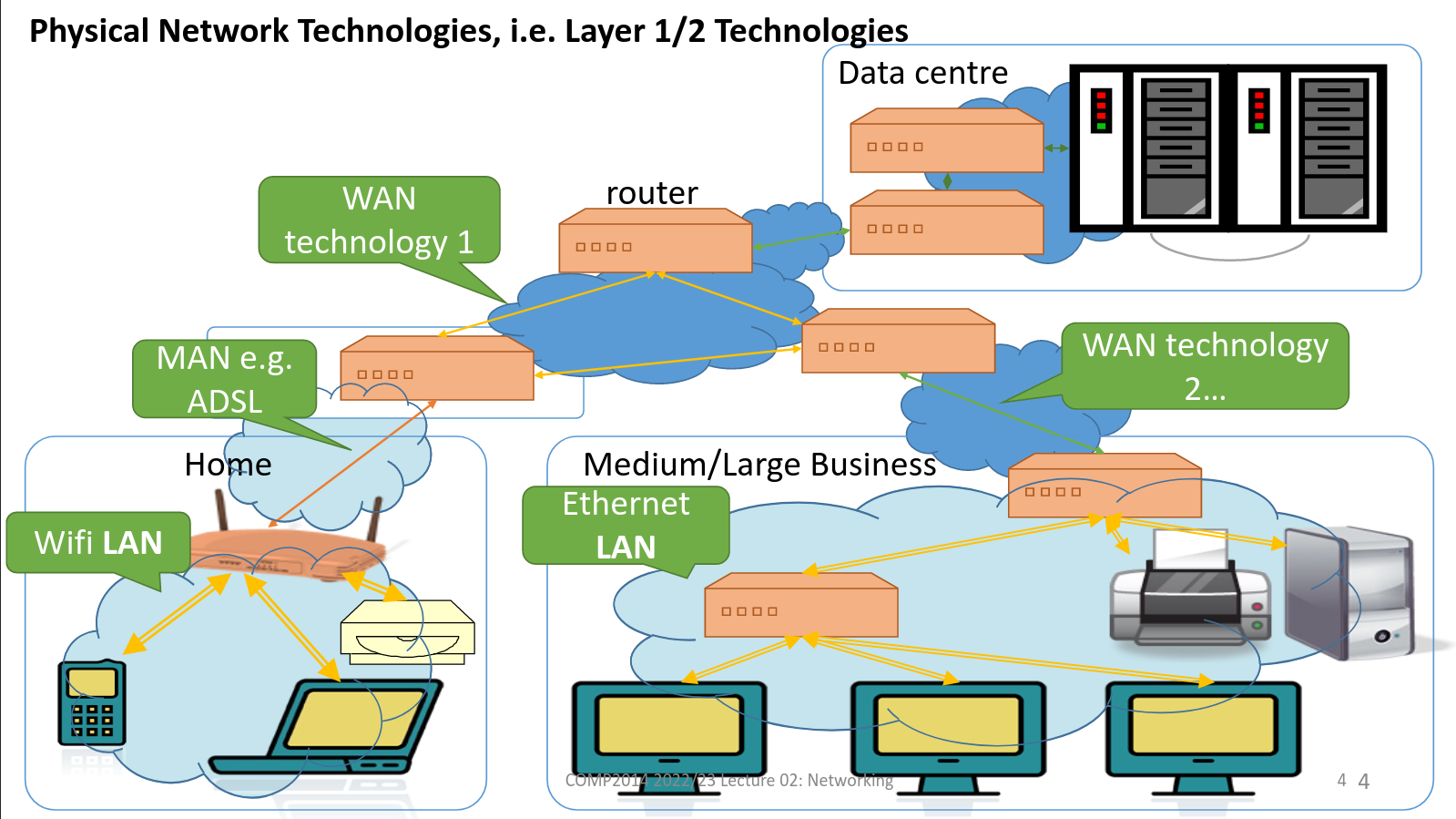
Layer1/2
- Each network can use a different technology, uses different bandwidth, latency and reliability.
- One computer can connect to several different networks
- Each network interface typically has its own layer 2 network address, often called a MAC(Medium Access Control) address.
- Some networks allow a single message to be physically sent to all machines on that network
The Internet: IP, TCP and UDP
Internet
- Illusion of a single network provided to users and applications.
- Underlying physical structure with routers interconnecting networks.i
- Based on specific layer 3 and layer 4 protocols plus supporting layer 5 protocols (DNS, routing)
- Provides a unifying pointer for almost any network application.
- Doesn't care what technologies/protocols it is built on (layers 1 and 2)
- Doesn't care what applications it is used for (layer 5)
Typical Network Protocol Stack
| Layer | Name | Common Protocol(s) | Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Application | HTTP, DNS(DHCP) ((routing)) | Application-specific |
| 4 | Transport | TCP, UDP | Generic packets and streams |
| 3 | Internet | IP(ICMP, ARP) | Global Communication |
| 2 | Network Interface (Link) | 802.11 - Ethernet, WiFi | Single hop (link) communication |
| 1 | Physical | Ethernet PHY, ADSL | Signals & physics |
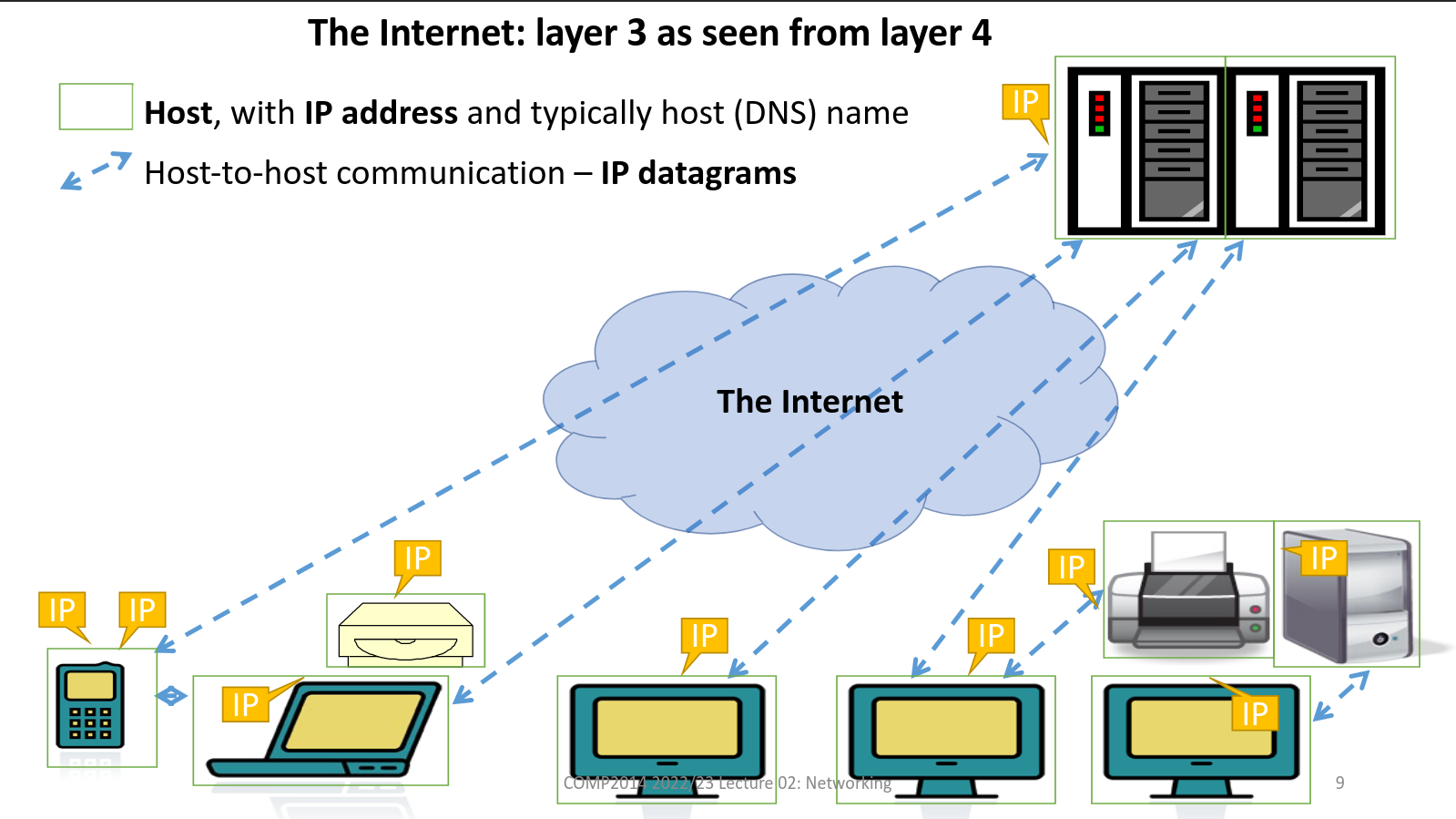
The Internet model
- Every networked machine is a node or host (has one or more IP addresses)
- Any machine can send a packet of data to any other machine (aka a datagram)
- Packets may be lost, delayed, corrupted or duplicated, although there is some checking for corrupted data. (Termed a best effort service)
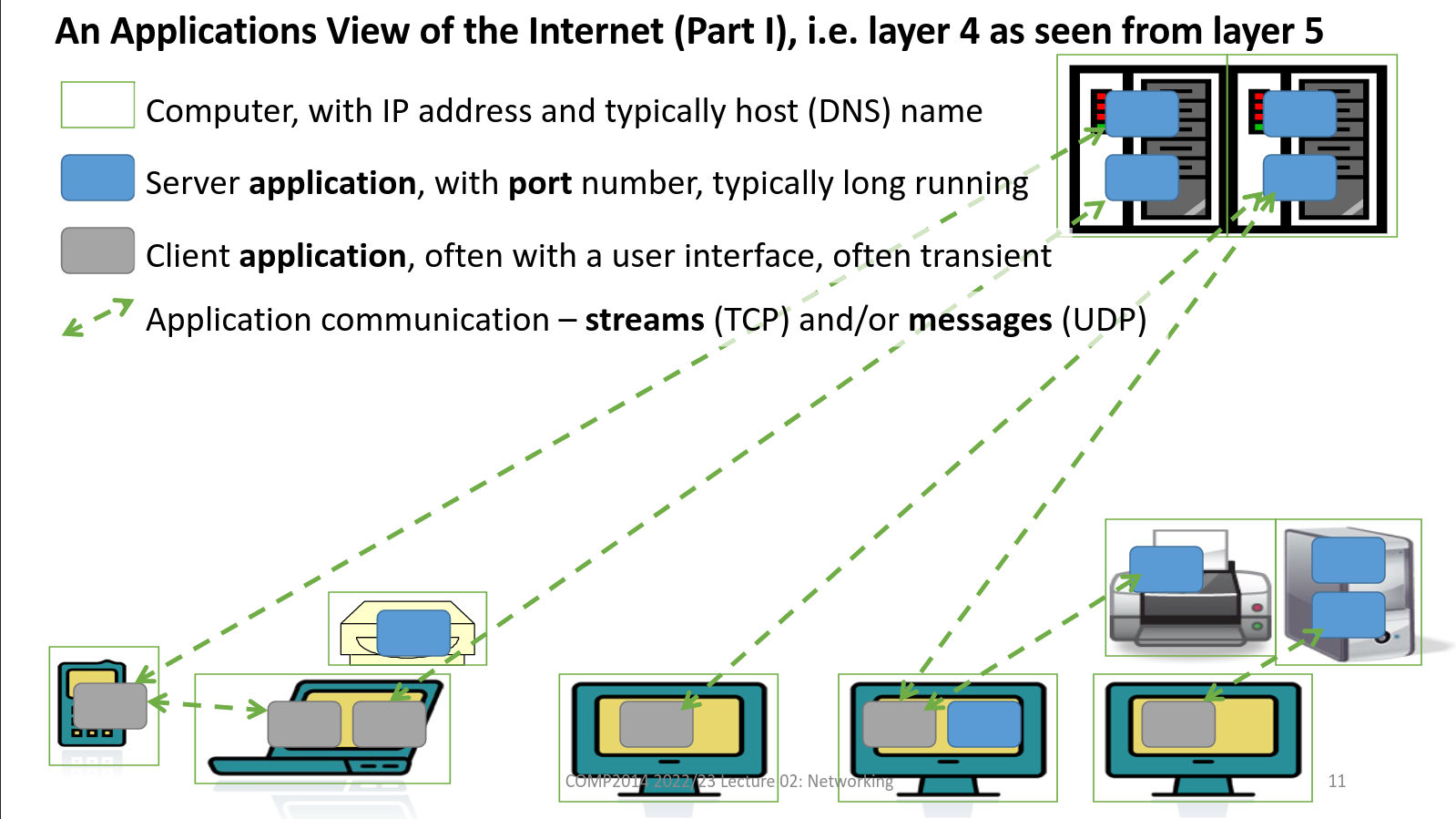
TCP and UDP: Streams and Messages
- Applications don't use IP directly. Use either TCP or UDP
- TCP - Reliable, bidirectional connection-oriented service for stream of bytes
- UDP - Best effort connectionless service for messages = packets of bytes. Uses IP directly and normally 1-1.
Routing and Configuration
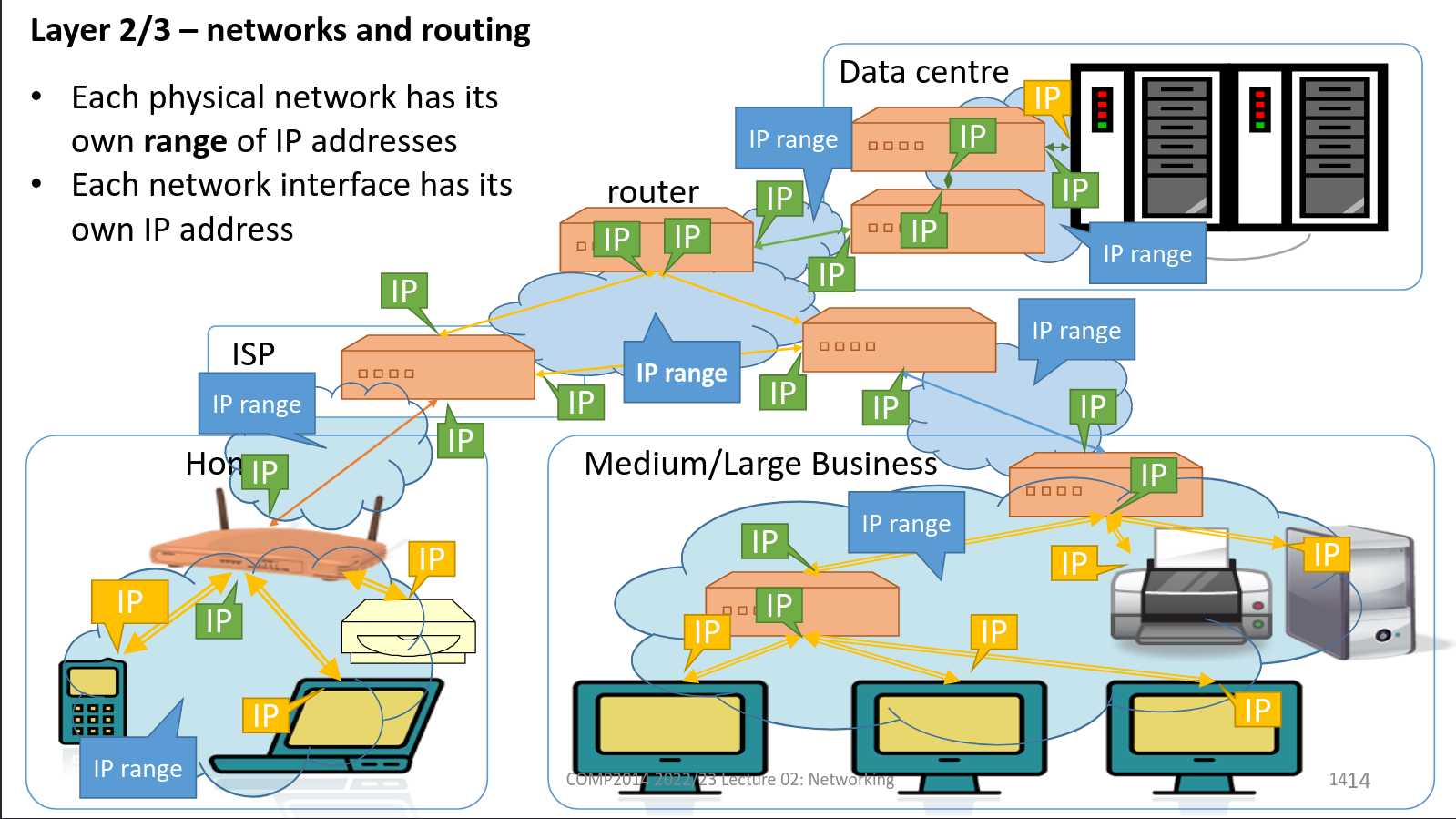
Routing and Forwarding
- Routers have interface on two or more networks and forward packets from one network to the next
- Have routing tables - identify for each destination IP address which interface/host to sent it to next
- Host and routers work together to deliver each packet to its destination
Host Configuration
- Every host needs to know
- Own IP address and the range on the network
- IP addresses of other routers(gateway) and the IP of the DNS
- Often discovered when the machine connects to a local network by using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).This provides the information
- Servers may be statically configured
Router Configuration
- Partly configured statically with IP address for each of its network interfaces and a range for each directly connected network
- Routers use routing protocols to exchange information with other routers
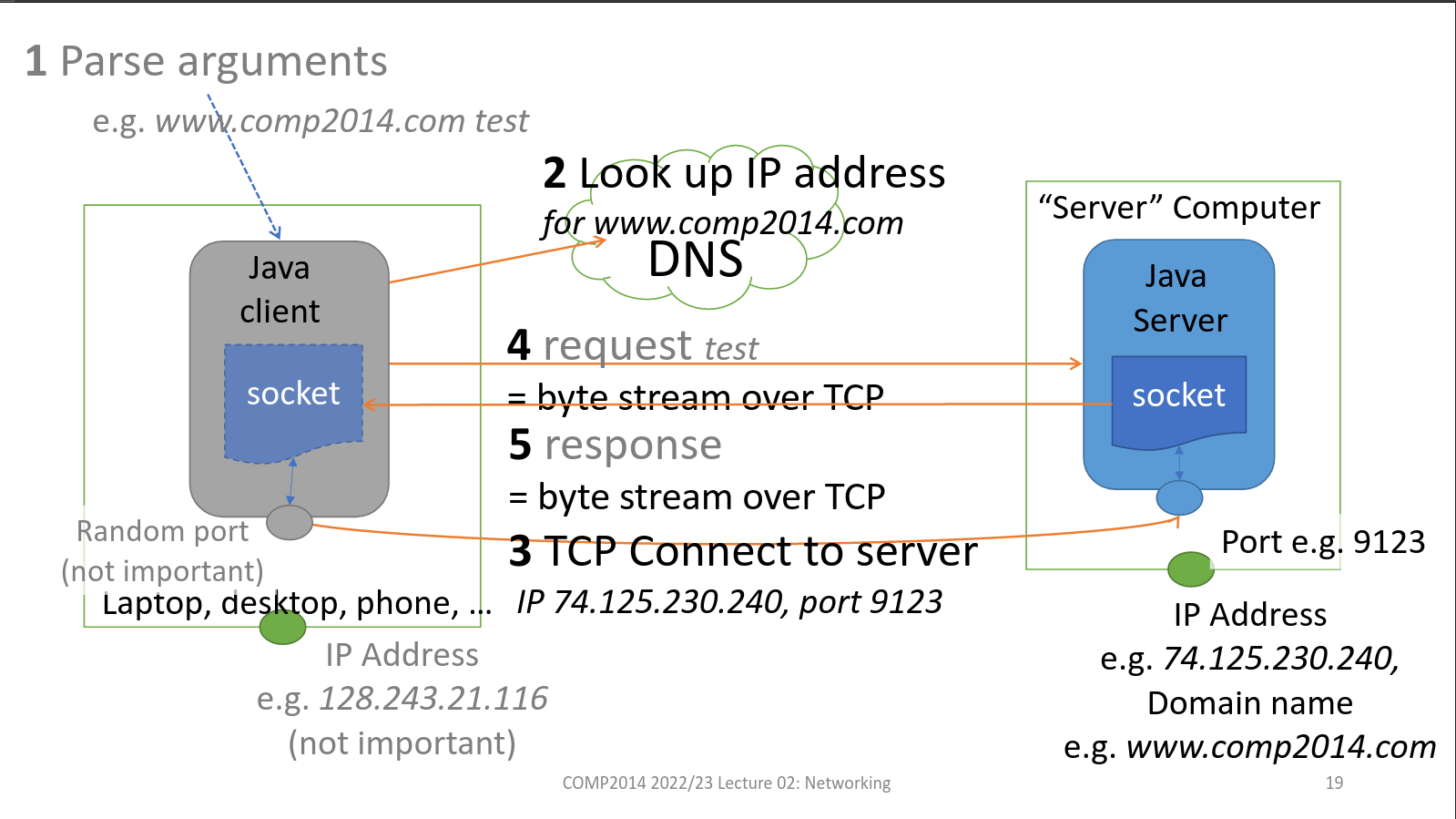
Java TCP Infographics
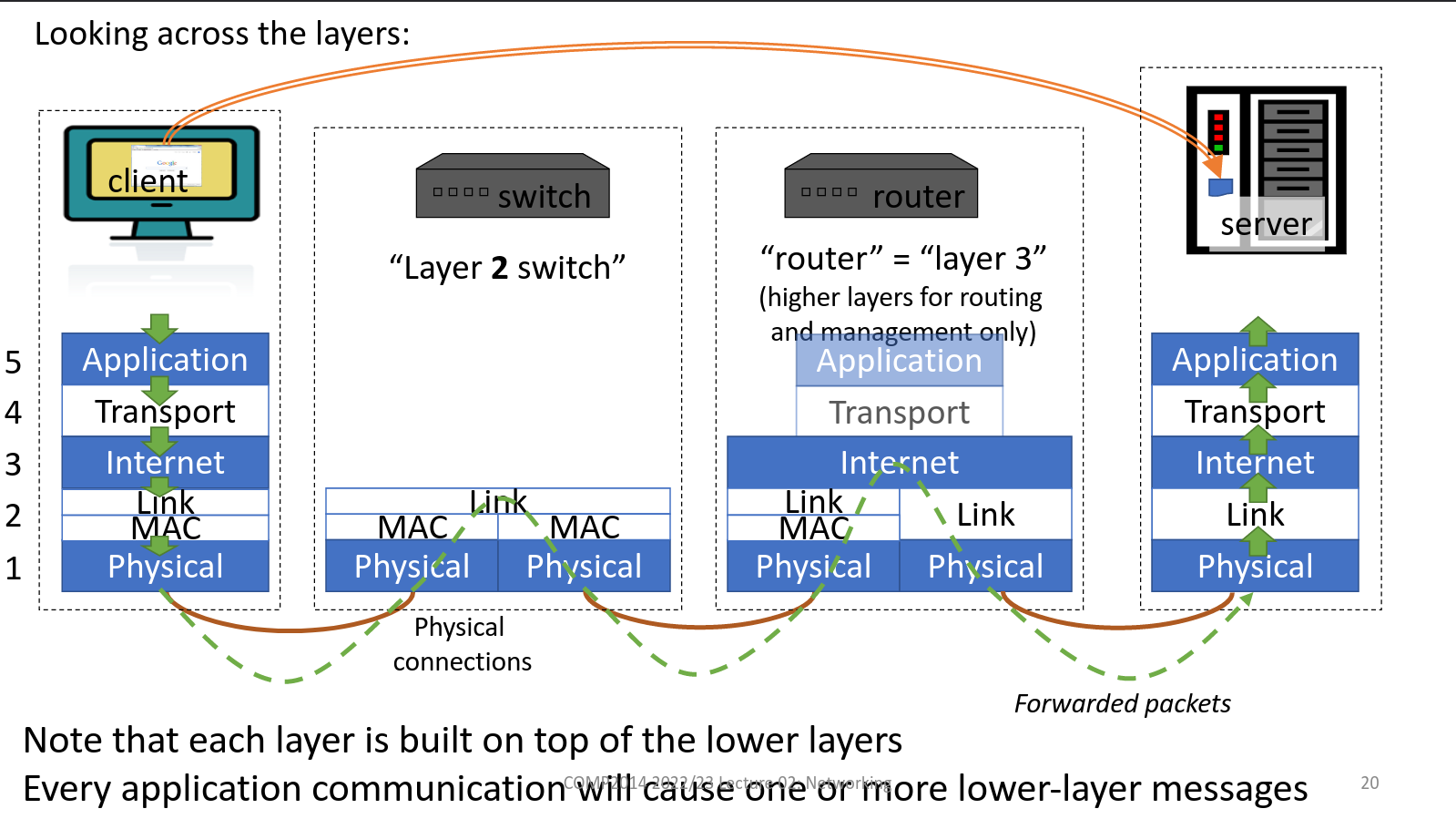
Virtual machines, containers, the cloud and SSH
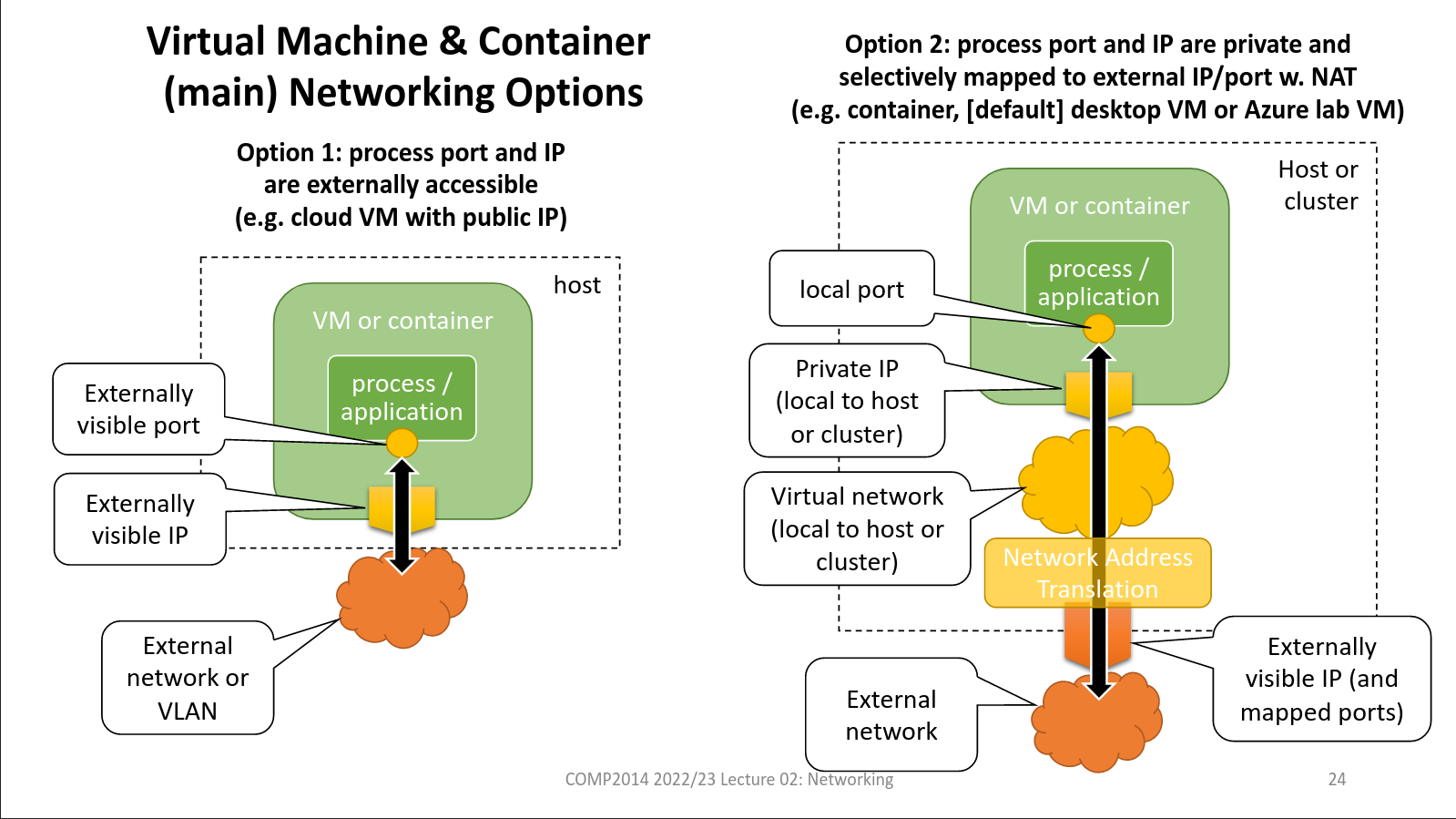
 Each VM or container has its own virtual network interface and IP address. These may be visible directly on the physical network or on the visualised one. Selected ports would be exposed through the Network Address Translation
Each VM or container has its own virtual network interface and IP address. These may be visible directly on the physical network or on the visualised one. Selected ports would be exposed through the Network Address Translation
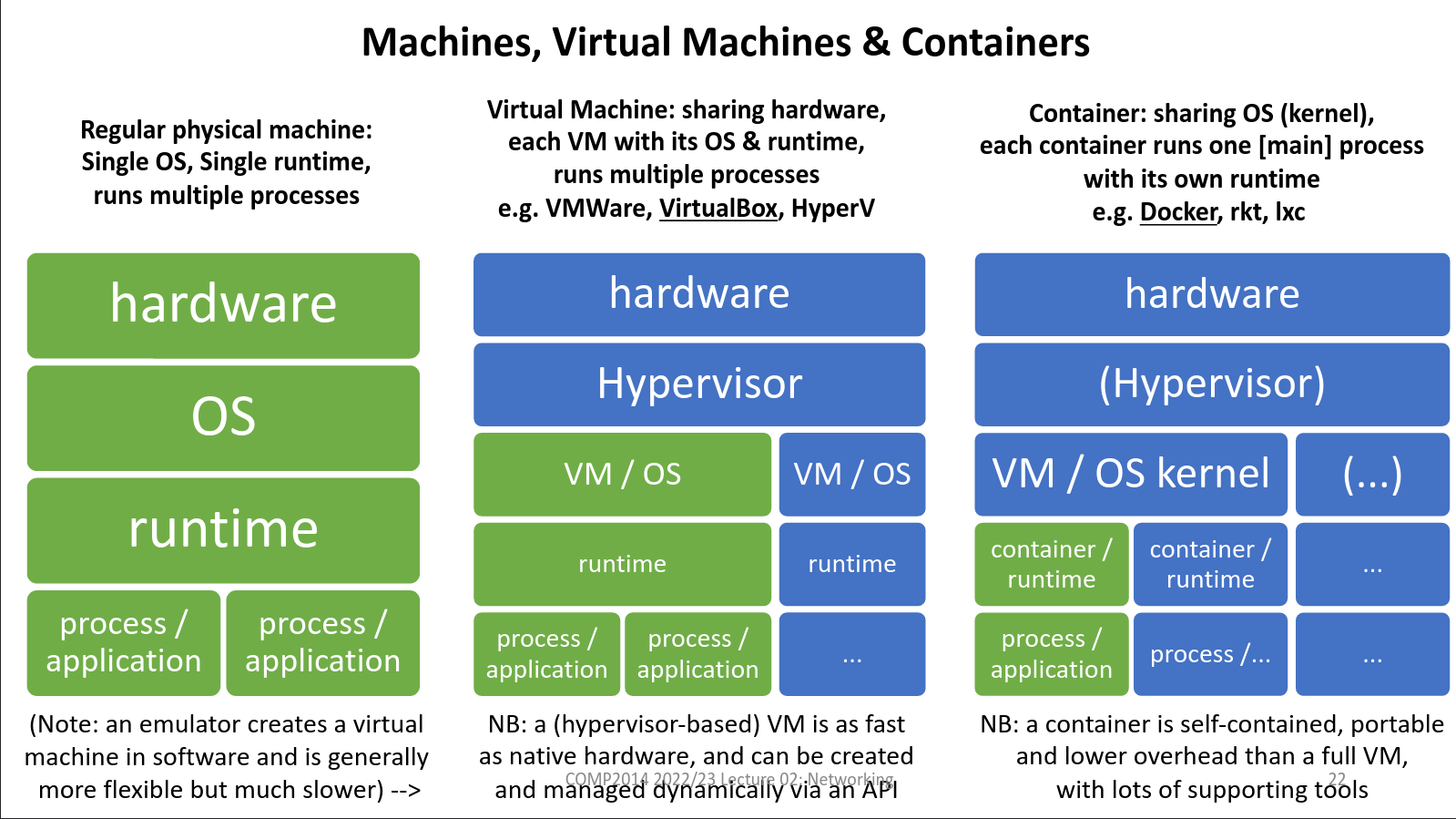
Hypervisor allows efficient virtualisation of a single computer to create multiple isolated Virtual Machines (VM).
The Cloud - Computing in remote data centres. Many services are available:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - Virtual machines, virtual disks
- Containers as a Service (CaaS) - Container hosting
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) - Language-specific application hosting
- Serverless - Auto scaling application or function hosting
- Software as a Service - End user applications (Office 365)
SSH - Network protocol allowing secure remote access. Creates an interactive shell.
Low-level Network Security
- Physical Layer, 1, deals with signals and direct physical communication.
- Network Interface (Link) Layer, 2, deals with single hop (link) communication. May have its own MAC addresses