Revision
Things to go over for DS
Nameserver - Stores the records of a DNS
Marshalling - Process of converting program data to network form (JSON)
NAT - Device change the local IP addresses and ports when they pass on packets
RPC - Pretend remote device is actually local. It is an interface. Call by reference parameter passing is not possible. (Must be pass by copy). Typically defined as an interface. Memory is not shared. Much slower and subject to failures
RMI - Applies RPC to objects.
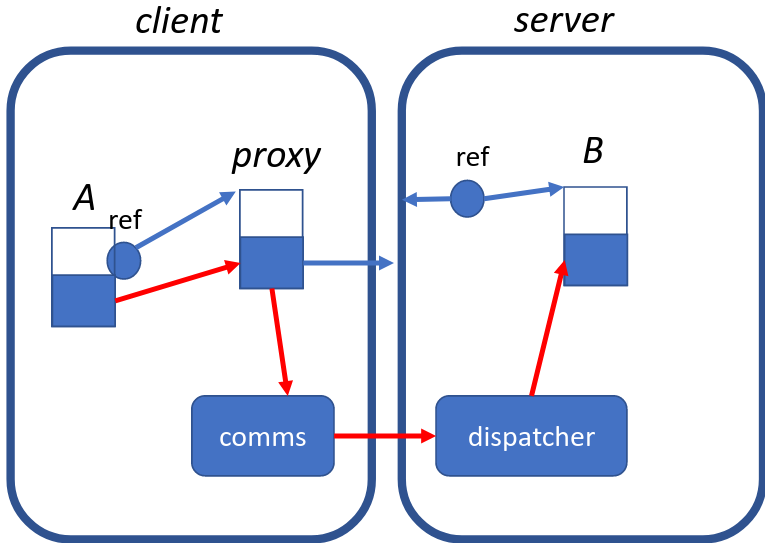
- REST
- Handling Requests
- Static file serving - the web server uses the URL path to identify a file which is copied back as the response body
- CGI - the server executes a program (identified by the URL) in a separate process to handle the request
- Dynamically loadable module - the server loads a runtime engine to execute a file in a scripting language
- Reverse proxy - the original server becomes an HTTP client to pass the request onto another web server
- Custom web server written using a language-specific web server framework - the web server includes the code to handle specific requests
- Architectural Models
- Proxy - Object/Service presents the same interface as a remote service but more locally, and passes on requests
- Broker - Common point where service providers can register their existence so that clients can find them
- Layering - Partitioned into a number of layers, with a given layer making use of the services offered by the layer below
- Tiered - System divided into distinct layers of tiers, each of which is comprised of specific processes
- Distributed System failures
- Heterogeneity - Coping with system component variability
- Failure Handling - Coping with partial failure
- Concurrency - Correctness and performance with concurrency
- Scalability - Able to adapt based on the current situation, being able to add or remove nodes
- Indirect Communication
- Space Uncoupling - The sender does not (need to) know the identity of the receiver and vice versa. (Partitions can be replaced, updated, replicated, migrated)
- Time Uncoupling - The sender(s) and receiver(s) can have independent lifetimes. E.g. in a volatile environment
- Group Communication
- Application-level abstraction of multicast communication. e.g. fault-tolerance, reliable distribution to large numbers
- Open-Group - Non-members can send to closed groups
- Non-overlapping groups - Each process can be a member of at most one group
- Synchronous group communication - Does a sender blocks until all group members have received the message/replied
- Reliability - Integrity (Message received is same as one sent), Validity (Outgoing msg is eventually delivered); Plus agreement (If the message is delivered to one process, then it is delivered to all processes in the group)
- Publish-Subscribe
- Publish info, and services subscribe. e.g. finance info, live feeds
- Characteristics: Heterogeneity, async, delivery guarantee
- Centralised event service - Relatively easy to construct, the event service becomes a bottleneck
- Distributed event service - More complex, but more scalable
- Event routing
- Flooding - Every event is sent to every event broker
- Filtering - Event brokers share subs info and forward events to where valid subs exist
- Rendezvous - There is a way to identify particular event brokers to handle matching events and subs
- Message Queues
- 1-1 communication
- Middleware
- Space uncoupled - Messages are sent via message queues
- Time uncoupled - message queues exist independently of message producers and consumers
- Operations
- Send - Add to queue
- Receive - Take from queue
- Poll - Check head of queue
- Notify - Inform consumer msg is available
- Usually persistent and reliable
- DSM
- System emulate shared memory between processes on different computers
- Tuple Spaces
- Write/read/take(read&delete)
- Read and take done by pattern matching
- Both space and time uncoupled
Content to revise from exam paper
- Nodes do not run an OS, run directly on the node hardware
- Replication - Send msgs to one another so theyre in sync
- For add, it would wait for responses from all the servers
- If server fails to respond, then marked as failed and carried out on a alternative server
- Procs and cons of REST
| Form Style | REST |
|---|---|
| + Works directly with form | - Requires AJAX or client |
| + Direct feedback to user | - ditto |
| - ad hoc signalling of errors to clients | +Easily extend interfaces |
| - Harder to type param | Standard ways to signal errors/ type param |
- Failures which can occur during RMI
- Process Failure - Server may have crashed (or been restarted)
- Network Failure - Network may become partitioned, or the loss rate too high to maintain the TCP connection
- TCP connection request would fail/time out, client runtime would throw a RemoteException
- Application specific errors
- Benefits of having 2 DNS administrative zones
- Can tolerate 1 server crashing or being unreachable, as other server can respond, but cant deal with both of them crash
- Setting up a server for Java RMI, need to register the object with the RMIRegistry using
java.rmi.Naming.rebindwith the new name
- Transactions: Assume the process can be trusted, there are no arbitrary failures and communication is reliable. Set aside a specialised coordinator process to coordinate the entire transaction. Broken into two sections; Tentatively, performing the operation. Making operation permanent by committing it.
- Partitions - Split up a network, either physically or virtually. This increases performance, enhances security, simplifies network management, and also compliance and regulatory requirements.
| Internet Model | |
|---|---|
| 5 | Application |
| 4 | Transport (TCP/UDP) |
| 3 | Internet (IP) |
| 2 | Network interface/Link |
| 1 | Physical |
- DNS Administrative Domain - Is a subset of namespace with a single administrative authority. Corresponds to a domain name suffix. Each authority has complete control over its own administrative zones.
- Name Server - Records identify responsible name servers
Things to look over
- DNS administration
- HTTP Request order thing (One of the past papers)