7. WWW and HTPP
28/02/23
The Word Wide Web and URLs
- WWW - Is a distributed system for publishing and accessing resources across the internet
- It is a client server system, web browsers are the commonest client
- Based on a request-response protocol (HTTP)
Web Protocols
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) - A transfer protocol that specifies how a browser interacts with a web server
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL) - Representation standard that specifies the format of web page identifiers
- HyperText Markup Language (HTML) - A representation standard that specifies the contents and layout of a web page
Browser: Handling a URL
- Divides the URL into protocol, computer name & port, document name, parameters
- Use the protocol to decide which protocol to use
- Use the computer name and protocol port to form a TCP connection to the server on which the page resides
- Use the computer name, document name and parameters to request a specific page from the server using HTTP
- Displays the content (or error) received from the server
Browser: URLs and Navigation
- Each tab in a browser is displaying the content retrieved from one URL
- URL can be changed by entering new url, hyperlink or code
- AJAX can also be used to make a http request in the background
HTTP
- Primarily transfer protocol that a browser uses to interact with a web server.
- HTTP is a request-response protocol
Methods
- GET - Requests a document; server sends a copy of the document
- HEAD - Request status information; server sends status (headers) only for the request document
- POST - Sends data to a server
- PUT - Server replaces the data
- DELETE - Request document be deleted
Response
- 200 - OK
- 400 - Bad Request
- 403 - Forbidden
- 404 - Not Found
- 301 - Moved
- 307 - Redirect
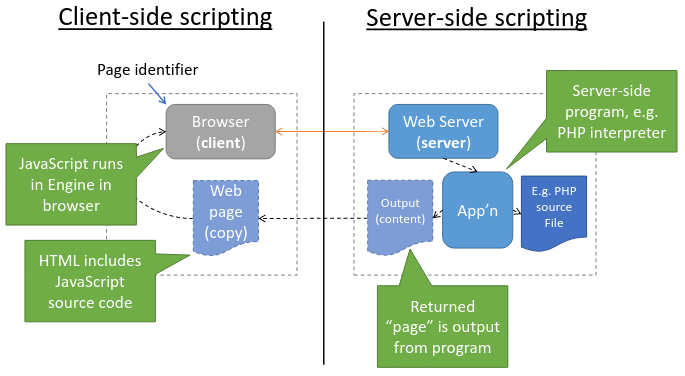
HTML & Scripting
- Representation standard that specifies the syntax of a web page for display in a browser
Client-side scripting - Embedded JavaScript which is run in the browser. Handle user input events, make HTTP requests, dynamically update the HTML.
Server-side scripting - HTML the server receives could be static or dynamically generated. (generated on-the-fly by running code on the server to handle)