11. Indirect Communication (2)
14/03/23
Message Queues
- Message queues (MQ) support 1-1 communication. (1-M of multicast & pub-sub)
- Space uncoupled - messages are sent via message queues
- Time uncoupled - message queues exist independently of message producers and consumers
- Also known as message-oriented middleware (MOM)
- Commonly used for integrating back-office systems
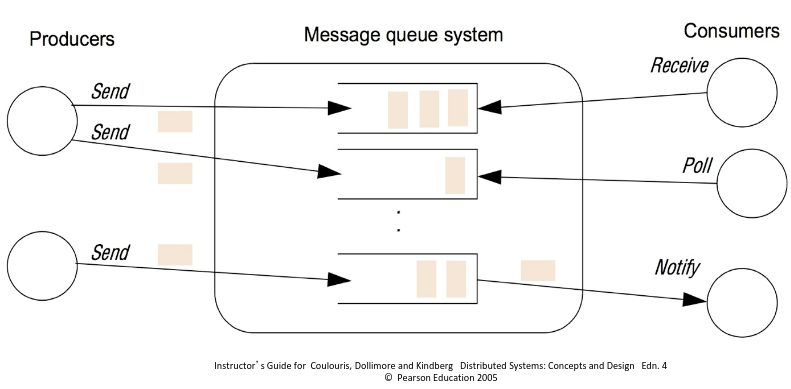
Message Queue Operations
- Send - add a message to a queue. Typically to the tail of the queue, can be configured
- Receive - Take a message from a queue. Typically head, can be configured
- Poll - Check head of queue without taking the message
- Notify - Inform a potential consumer that a message is available
Implementation Notes
- Messages typically comprises of:
- Destination - identifying the queue
- Metadata or header - priority, delivery mode
- Body - payload or content of message
- Message queues are typically persistent and reliable
Java Messaging Service (JMS) is a common API specification
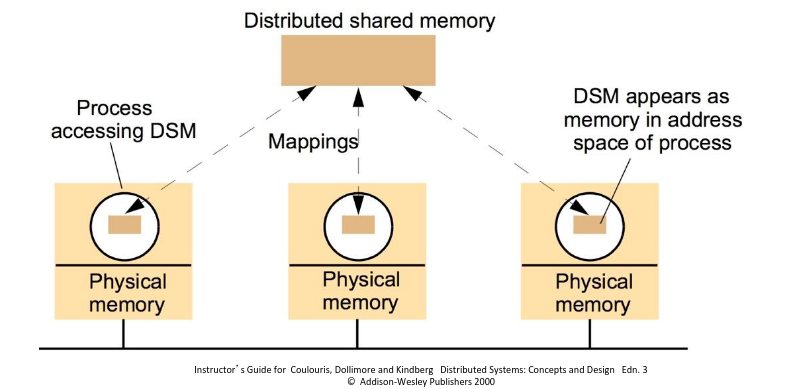
Distributed Shared Memory
- DSM systems emulate shared memory between processes on different computers
- The DSM system sends messages between nodes to maintain a consistent view of memory
- Much slower than local shared memory
- Typically requires additional disciplines such as use of locks
Tuple Spaces
- Several processes can share a single tuple space
- Similar to distributed shared memory
- All values are tuples
- Tuples can be written to (write), read from (read) or taken from (take = read and delete) the tuple space
- Reads and takes are done by pattern matching
Characteristics
- Like message queues, tuple spaces are both space uncoupled and time uncoupled
- (many) Tuple spaces can also support transactions
- automatically group a sequence of read/take.write operations
JavaSpaces is a tool for tuple space communication part of JINI. Strictly is an object space
Example: Redis
- Is an in-memory data structure store, used as a database, cache, and message broker
- Provides data structures
- Each data-structure is identified by a key